Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
December 2023
Ducktail malware: what is it and why are businesses so concerned about it?
The number of new types of attacks that compromise organizations’ cybersecurity is on the rise. Cybercriminals are more capable than ever of adapting and upgrading their attack formats to circumvent their victims' protection protocols. Data shows that the volume of new attacks is increasing every year. According to Astra, this year we have reached a record number of 560,000 new types of malware detected daily. This brings the number of malware currently in existence to over one billion.
U.K. Government 'Ill-Prepared' to Deal With High Risk of Catastrophic Ransomware Attacks
A new report from the U.K. government’s Joint Committee on the National Security Strategy (JCNSS) outlines both just how likely an attack on critical national infrastructure is and where they are vulnerable. The impact of a coordinated cyberattack on the U.K.’s national infrastructure could impact millions of citizens within its country, according to the JCNSS’s report A hostage to fortune: ransomware and UK national security.
PoolParty Process Injections, SysJoker, NetSupport RAT, & More: Hacker's Playbook Threat Coverage Round-up: December 2023
In this version of the Hacker’s Playbook Threat Coverage round-up, we are highlighting attack coverage for newly discovered or analyzed threats, including those based on original research conducted by SafeBreach Labs. SafeBreach customers can select and run these attacks and more from the SafeBreach Hacker’s Playbook™ to ensure coverage against these advanced threats. Additional details about the threats and our coverage can be seen below.
How Malicious Code Enters Applications
As the backbone of modern business operations, applications are frequently targeted by sophisticated malicious threats. In this blog post, we provide a high-level overview of how malicious code can enter your software applications. We look at different forms of malicious code, their entry points, practical tools and strategies for detection & prevention, focusing on innovative solutions.
Top 3 Office 365 Backup solutions for 2024
Ransomware Attacks Rise 85% Compared to the Previous Year
With November demonstrating multiple increases when compared to various previous time periods, new data signals that we may be in for a bumpy ride in 2024. It’s nice when we get to see reports that are published relatively quickly to let us get a sense of where cyberattacks are today versus, say, a quarter or two ago (or even last year!). The NCCGroup’s Cyber Threat Intelligence Report was just published and covers ransomware attacks through November of this year.
Ransomware Criminals Steal 2.7 Million Records from Emergency Software
ESO Solutions is a primary software developer and analytics platform for emergency and associated services; its programs connect emergency response agencies, fire departments, hospitals, and state response offices. ESO collects and disperses data between the services, giving responders the most complete information.
Snatch Ransomware: Digital Cat and Mouse
Predict the Future! A universal approach to detecting malicious PowerShell activity
So, here’s the deal with AntiVirus software these days: It’s mostly playing catch-up with super-fast athletes — the malware guys. Traditional AV software is like old-school detectives who need a picture (or, in this case, a ‘signature’) of the bad guys to know who they’re chasing. The trouble is, these malware creators are quite sneaky — constantly changing their look and creating new disguises faster than AntiVirus can keep up with their photos.
CTI Roundup: TA4557, OAuth Cryptomining, and the China-based KEYPLUG backdoor
TA4557 targets recruiters via email, threat actors use OAuth apps to automate BEC and cryptomining attacks, and researchers discover Sandman APT’s connection to the China-based KEYPLUG backdoor.
TEMU phishing attacks using spyware up 112% in the run up to Christmas
As the most downloaded app in the world right now, the number of TEMU impersonation emails has increased by 112% since October 1st, 2023. As discounts and spending-based reward coupons form a substantial part of TEMU’s awareness campaigns, the company is reportedly spending $2bn annually on marketing. As the brand continues to grow in popularity, cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging it to lend authenticity to their spoofing attempts.
A Look at the Nim-based Campaign Using Microsoft Word Docs to Impersonate the Nepali Government
Threat actors often employ stealthy attack techniques to elude detection and stay under the defender’s radar. One way they do so is by using uncommon programming languages to develop malware. Using an uncommon programming language to develop malware provides several benefits, including: Netskope recently analyzed a malicious backdoor written in Nim, which is a relatively new programming language.
"Mr. Anon" Infostealer Attacks Start with a Fake Hotel Booking Query Email
This new attack is pretty simple to spot on the front, but should it be successful in launching its’ malicious code, it’s going to take its’ victims for everything of value they have on their computer. The new Mr. Anon infostealer captures much more than just browser caches and passwords. It also uses basic social engineering tactics that prove to be effective enough to make attacks successful.
An Analysis of Menorah Malware
SecurityScorecard is analyzing a phishing campaign that deployed the Menorah malware, which is taking aim at users in the Middle East. This sophisticated campaign is being mounted by the threat actor group tracked as APT34, which is linked to Iran. This group is known for its focus on collecting sensitive intelligence and taking on high-profile targets across the Middle East including critical infrastructure and telecommunications entities.
TargetCompany Ransomware Group AKA Mallox: A Rapid Evolution
Play Ransomware: SafeBreach Coverage for US-CERT Alert (AA23-352A)
On December 18th, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and Australian Signals Directorate’s Australian Cyber Security Centre (ASD’s ACSC) issued an urgent advisory to highlight the ongoing malicious activities being conducted by the Play ransomware group.
Netskope Threat Labs Stats for November 2023
Netskope Threat Labs publishes a monthly summary blog post of the top threats we are tracking on the Netskope platform. The purpose of this post is to provide strategic, actionable intelligence on active threats against enterprise users worldwide.
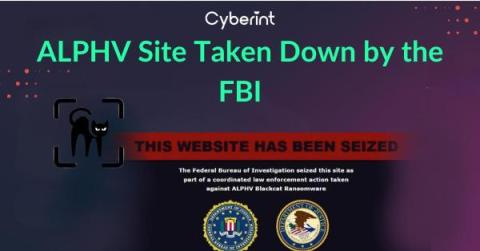
ALPHV Site Taken Down by the FBI
Unique Malware Used in Cyber Attacks Increases by 70% in Just One Quarter
As more cybercriminal gangs continue to enter the game, the massive increase in unique types of malware means it will become increasingly difficult to identify and stop attacks. Blackberry just put out their Global Threat Intelligence Report in November, covering June through August of this year. According to the report, the number of attacks identified and stopped in the three-month period covered equates to an average of 26 attacks per minute.
Conversations with Charlotte AI: "What is my exposure to vulnerabilities used by Scattered Spider?"
Detect & Recover From VM Encryption Attacks With Rubrik
Behind the Scenes: JaskaGO's Coordinated Strike on macOS and Windows
In recent developments, a sophisticated malware stealer strain crafted in the Go programming language has been discovered by AT&T Alien Labs, posing a severe threat to both Windows and macOS operating systems. As of the time of publishing of this article, traditional antivirus solutions have low or even non-existent detection rates, making it a stealthy and formidable adversary.
Honeypot Recon: MySQL Malware Infection via User-Defined Functions (UDF)
In the vast world of cybersecurity, as technologies evolve, so do the methods attackers employ to compromise systems. One such intriguing method that recently surfaced is MySQL servers, leveraging SQL commands to stealthily infiltrate, deploy, and activate malicious payloads. Let's delve deeper into the MySQL bot infection process and explore the intricacies of its operation.
Defend yourself and your vendors against ransomware
What Is Ransomware as a Service?
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) is a business model in which cybercriminals develop and sell ransomware to buyers known as affiliates who use it to execute ransomware attacks. Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents users from accessing their data or devices by encrypting them and locking users out until a ransom is paid. Typically, cybercriminals need to know some coding to develop and execute ransomware attacks.
Las Vegas casinos targeted by ransomware attacks
Ever since the invention of internet browsers for personal computers came about in the 1990s, cybercrime has been on the rise. Almost 30 years after the invention of the Worldwide Web, cybercriminals have a variety of different methodologies and toolkits that they use on a daily basis to leverage vulnerabilities and commit crime. One of the most popular types of attacks that is used by threat actors is a ransomware attack.
BlackSuit ransomware - what you need to know
A cybercriminal group calling itself BlackSuit has claimed responsibility for a series of ransomware attacks, including breaches at schools in central Georgia. And earlier in the year, a zoo in Tampa Bay was targeted by the same hacking gang.
7 Practical Steps to Protect from Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba)
The Alarming Threat of Ransomware: Insights from the Secureworks State of the Threat Report 2023
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the battle against ransomware has taken a concerning turn. According to the latest findings from Secureworks annual State of the Threat Report, the deployment of ransomware is now occurring within just one day of initial access in more than half of all engagements.
New York Unit of Worlds Largest Bank Becomes Ransomware Victim
The ransomware attack on ICBC Financial Services caused disruption of trading of U.S. Treasuries and marked a new level of breach that could have massive repercussions. When we saw the attack on the Colonial Pipeline back in 2021, the impact was felt throughout the Southeast United States. Any attack on key businesses that keeps an economy running will have some form of impact should the attack be successful.
Understanding Polymorphic Viruses and Their Impact on Cybersecurity
Trustwave SpiderLabs Report: LockBit 3.0 Ransomware Vs. the Manufacturing Sector
As the manufacturing sector continues its digital transformation, Operational Technology (OT), Industrial Control Systems (ICS), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) are becoming increasingly exposed to cyberattacks, particularly those involving ransomware.
Why Ransomware Actors Abuse Legitimate Software
2023 was a lucrative year for ransomware actors, with victim organizations paying $449.1 million in the first six months alone. Maintaining this cash stream requires frequent technique shifts, which may be why more attackers are exploiting legitimate software to propagate their malware. Abusing organizations’ existing enterprise tools can help attackers blend in while they’re doing reconnaissance, and also aids them with privilege escalation and persistence.
Unmasking the Enigma: A Historical Dive into the World of PlugX Malware
Supply-chain ransomware attack causes outages at over 60 credit unions
Over sixty credit unions across the United States have been taken offline following a ransomware attack at one of their technology providers - demonstrating once again the damage that can be caused by a supply-chain attack. There are a few moving parts here, so here’s a quick summary: Trellance - A provider of solutions and services used by credit unions, and the parent company of FedComp. FedComp - a provider of software and services that enable credit unions to operate around the world.
Cloud Threats Memo: A Parasite Exploiting Legitimate Cloud Services
Malicious browser extensions are a common attack vector used by threat actors to steal sensitive information, such as authentication cookies or login credentials, or to manipulate financial transactions.