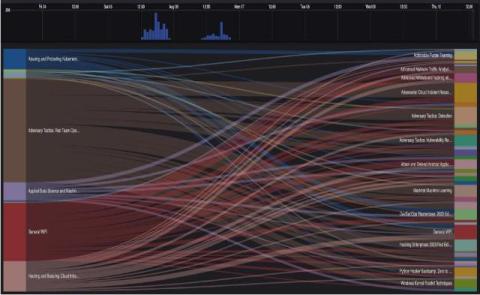
What Is EDR Security?
Back in 2013, Gartner’s Anton Chuvakin set out to name a new set of security solutions to detect suspicious activity on endpoints. After what he called, “a long agonizing process that involved plenty of conversations with vendors, enterprises, and other analysts,” Chuvakin came up with this phrase: endpoint threat detection and response.