Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
March 2022
How to Meet Third-party Risk Requirements in NIST 800-53
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has responded to the increased prevalence of third-party risks by specifying industry standards for securing the supply chain attack surface - the attack surface most vulnerable to third-party risks.
Things to Remember While Scaling Your Business
Driving Business Results with a Strategic Approach to Risk - and with ZenRisk
Cybersecurity Risk Management: Introduction to Security Analytics
Working with At-Risk Businesses: How It Can Dismantle Your Zero Trust Strategy
Nowadays, building a zero-trust network has become a standard protocol in the era of evolving business models, multiple workforce platforms, cloud adoption, and increased device connectivity. But, if a business continues to work with at-risk organizations, the zero-trust policy crumbles. Working with well-secured third parties that uphold a zero-trust strategy is crucial for optimal cybersecurity within any business.
Operationalize Risk and Compliance with the Reciprocity ROAR Platform
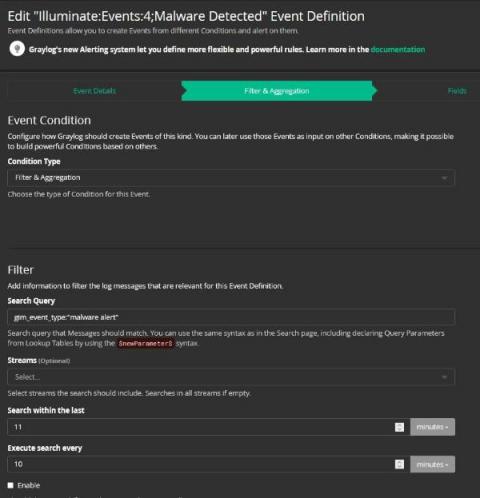
How to Mitigate Risks in Software Supply Chain Security
Move aside, Conti, Lapsus$ coming through!
-In the hours after news broke that Lapsus$ claimed to have breached Okta, an enterprise identity and access management firm, SecurityScorecard’s Threat Research and Intelligence team conducted a rapid investigation into Lapsus$ to provide customers and partners with the very latest in actionable security intelligence and insights related to this emerging cybercrime group. -Lapsus$’s targets have quickly evolved from Brazilian and Portuguese organizations to high-profile U.S.
SEC's Proposed Disclosure Amendments: Are You Impacted?
On March 9, 2022, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) announced proposed rules and amendments to enhance and standardize disclosures regarding cybersecurity risk management, strategy, governance, and incident reporting. These proposed amendments impact all public companies subject to the reporting requirements of the Security Exchange Act of 1934. To summarize this proposal and learn how to successfully prepare for them, read on.
How Managed Risk Best Addresses the Three Pillars of Cybersecurity
What Sets SecurityScorecard Apart!
The 3G network shutdown impacts more than just phones
As you have probably heard, 3G is phasing out. On February 22, AT&T shut down its 3G network. T-Mobile Sprint will retire its 3G network next week on March 31, 2022. Verizon, the last of the pack, will retire 3G by the end of 2022. What does this mean for your business and your security? The obvious answer is that older phones should be replaced as soon as possible, but the 3G shutdown’s impact will reach beyond phones, and that reach may affect your organization’s security.
Security Ratings Demystified
Alleged Okta Breach - What Can You Do?
Early in the morning of March 22nd a threat group known as LAPSUS$ posted screenshots on their Telegram account that allegedly show access to Okta internal systems such as Slack, Cloudflare, Jira, Salesforce and other “Okta cards.” Okta’s CEO Todd McKinnon apparently confirmed an event in January in a tweet:: “In late January 2022, Okta detected an attempt to compromise the account of a third party customer support engineer working for one of our subprocessors.
Building a risk management program? Start with compliance - and Reciprocity ZenComply.
4 Key Elements of A Good Cyber Hygiene
Top Recent Third-Party Breaches
The average company can’t do business without their third parties. Vendors, suppliers, partners, distributors, and contractors — third parties make it so much simpler to build, distribute and sell a product or service.
Meeting ISO 27001 Third-Party Risk Requirements
ISO 27001 compliance provides greater assurance that an organization is adequately managing its cybersecurity practices, such as protecting personal data and other types of sensitive data. Third-party risk management (TPRM) programs can benefit immensely from implementing the relevant ISO 270001 controls to mitigate the risk of significant security incidents and data breaches.
How to Prevent Whaling Attacks: A Complete Guide
Senior-level executives handle sensitive data and information daily – making them an enticing target for cybercriminals. One of the most complex schemes to date is the whaling attack, in which hackers impersonate high-ranking employees to gain access to computer systems and networks. Whaling attacks have seen a dramatic 131% increase between Q1 2020 and Q1 2021, costing enterprises around $1.8 billion in damages.
What Are Attack Surfaces and How to Protect Them
Banish Shadow IT With Digital Footprint
It’s out there. In the deep, dark corners of your IT estate, it’s been hiding. Maybe it’s that “killer app” one of the department heads brought back from a trade show. Or maybe it’s that campaign microsite that marketing had a contractor develop for a “skunkworks” launch. Shadow IT is more than an asset management problem. It’s a security problem because you can’t secure what you can’t see.
This Is the Reason Behind 70% Of Data Breaches
SecurityScorecard Discovers new botnet, 'Zhadnost,' responsible for Ukraine DDoS attacks
SecurityScorecard (SSC) has identified three separate DDoS attacks which all targeted Ukrainian government and financial websites leading up to and during Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Details of these DDoS attacks have not yet been publicly identified.
Understanding the Basics of Cyber Insurance: What You Need to Know
Data breaches and cybercrime are all too common. And in recent years, ransomware attacks have caused many organizations to face hefty extortion payments, legal fees, and reputational damage – not to mention the major headache that comes with each. Cyber insurance has become a powerful tool in the world of cyberattacks to help protect organizations from the implications of a ransomware attack, but many don’t understand what a cyber insurance policy actually covers.
Breach Costs - Millions of Lost Revenue
At the end of 2021, Capital One agreed to pay a settlement of $190 million to 98 million customers whose personal data was stolen in a 2019 data breach. Similar class-action lawsuits were filed in 2021 against T-Mobile, Shopify, and Ledger. When it comes to the cost of breaches, however, those are just the legal fees. Every year, businesses lose millions of dollars in revenue to cyberattacks and data breaches.
Improving FedRAMP: Federal Procurement & Risk Management
The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) has been in place for just over a decade (2011). Its purpose is to provide a “cost-effective, risk-based approach for the adoption and use of cloud services” by the federal government. This is to equip and enable federal agencies to utilize cloud technologies in a way that minimizes risk exposure through security and protection of federal information and processes.
Mitigating Risks in Software Supply Chain
What's new in UpGuard // Cyber Vendor Risk Management Product Releases
Strategies For Vendor Third Party Risk Management
How to Protect From Potential Cyber Threats Stemming From Russian/Ukrainian Crisis
Fireside Chat with UpGuard's CISO - Phil Ross & CMO - Kaushik Sen
VIP Identity Breaches Demo with UpGuard's Senior Product Manager, Chris Schubert
Vendor Risk Management - Cybersecurity Expert Panel
Product Spotlight with UpGuard's Chief Product Officer, Dan Bradbury
Risk Assessment Workflow Demo with UpGuard's Senior Product Manager, Chris Schubert
Slack Connector Demo with UpGuard's Senior Product Manager, Chris Schubert
Gain a full view of your vendor ecosystem with Automatic Vendor Detection
What is Cyber Hygiene? Definition, Benefits, & Best Practices
You’ve likely been practicing good personal hygiene since childhood, but have you heard of cyber hygiene? Similar to personal hygiene practices which maintain good health and well-being, cyber hygiene practices maintain the health and well-being of your sensitive data and connected devices. This blog will define cyber hygiene, discuss the importance of maintaining cyber hygiene and explore best practices for ensuring cybersecurity.