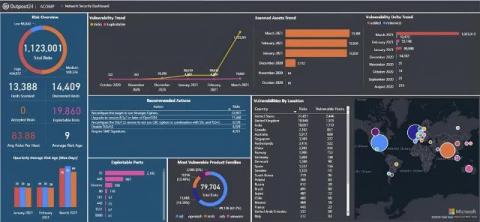
Belsen Group: Analyzing a new and ambitious threat group
On January 14th, 2025, Belsen Group emerged in the underground forum Breach Forums publishing a list of sensitive data extracted from vulnerable Fortinet FortiGate devices. Since then, they have expanded their malicious activities into acting as initial access brokers. Who are they and what do we know about them? In this blog we’ll give you the lowdown on an ambitious new threat group to be aware of.