Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
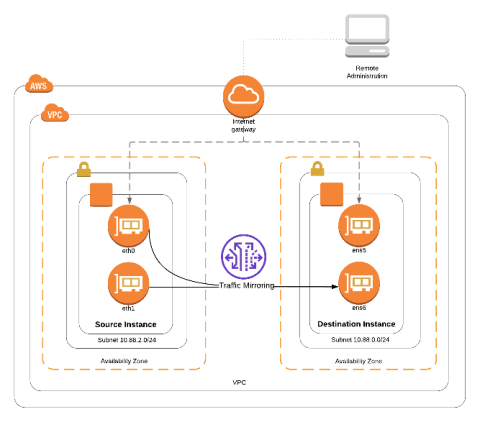
Networks
RDS: Do Not Allow LPT Port Redirection
vPenTest: Real-Time and Automated Network Penetration Test Platform
RDS: Do Not Allow COM Port Redirection- The Policy Expert
The Policy Expert: MMS: IP Source Routing Protection Level
The risks of public Wi-Fi and how to stay safe
In a bid to entertain their customers, airports, coffee shops, shopping malls - and literally all public places- provide free Wi-Fi. And because the traffic in and around these places is exceedingly high, their Wi-Fi networks aren’t as secure as you’d imagine. For what it is worth, your privacy can never be sufficiently protected by a 5 or even 10-digit login password that you are given.
Tracking Malicious Activity across the Sumo Attack Lifecycle
What is Network Security?
Network security is the process of using physical and software security solutions to protect the underlying network infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, malfunction, modification, destruction or improper disclosure, creating a secure platform for computers, users and programs to perform their functions in a secure environment.
Undivided we fall: decoupling network segmentation from micro-segmentation in the software defined perimeter
As of today, no laws or regulations, even the latest version of PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and HITECH, do not make network segmentation or micro-segmentation compulsory to comply with the rule. By making network segmentation discretionary -- even when transmitting, processing, or storing regulated data, the number of breaches will continue to rise as companies err on the side of doing less with more.
DNSSEC: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
The Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC or DNS Security Extensions) is a set of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) specifications for securing certain kinds of information provided by the Domain Name System (DNS) as used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks. DNSSEC provides DNS resolvers origin authentication of DNS data, authenticated denial of existence and data integrity but not availability or confidentiality.