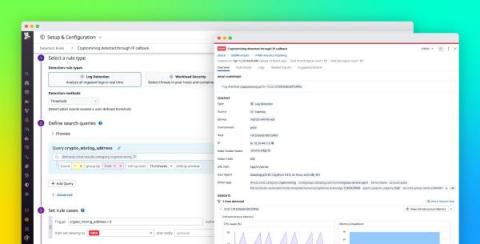
Detect cryptocurrency mining in your environment with Datadog Cloud SIEM
Cryptocurrency mining (or crypto mining) can be a lucrative yet resource-intensive operation, so cyber threat actors are targeting more organizations in order to take advantage of their cloud resources for mining. Datadog Cloud SIEM can now help you monitor your cloud-based systems for unwanted crypto mining via a built-in detection rule. All you need to get started is to configure your resource logs with Datadog’s @network.client.ip standard attribute.