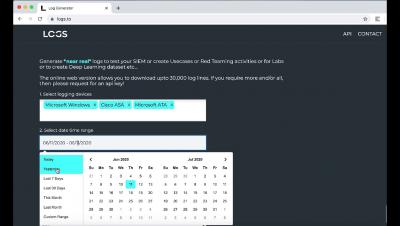
3 signs it's time to relook your approach to security operations
Security operations centers monitor and analyze activities on networks, servers, databases, applications, websites, and other systems, looking for anomalous activity that could be indicative of a security incident or compromise. Alert fatigue is a growing concern among information security professionals. If statistics are to be believed, over 79% agree about its negative effects on their teams.