Unveiling The Surge: Rising Car Insurance Costs In 2025
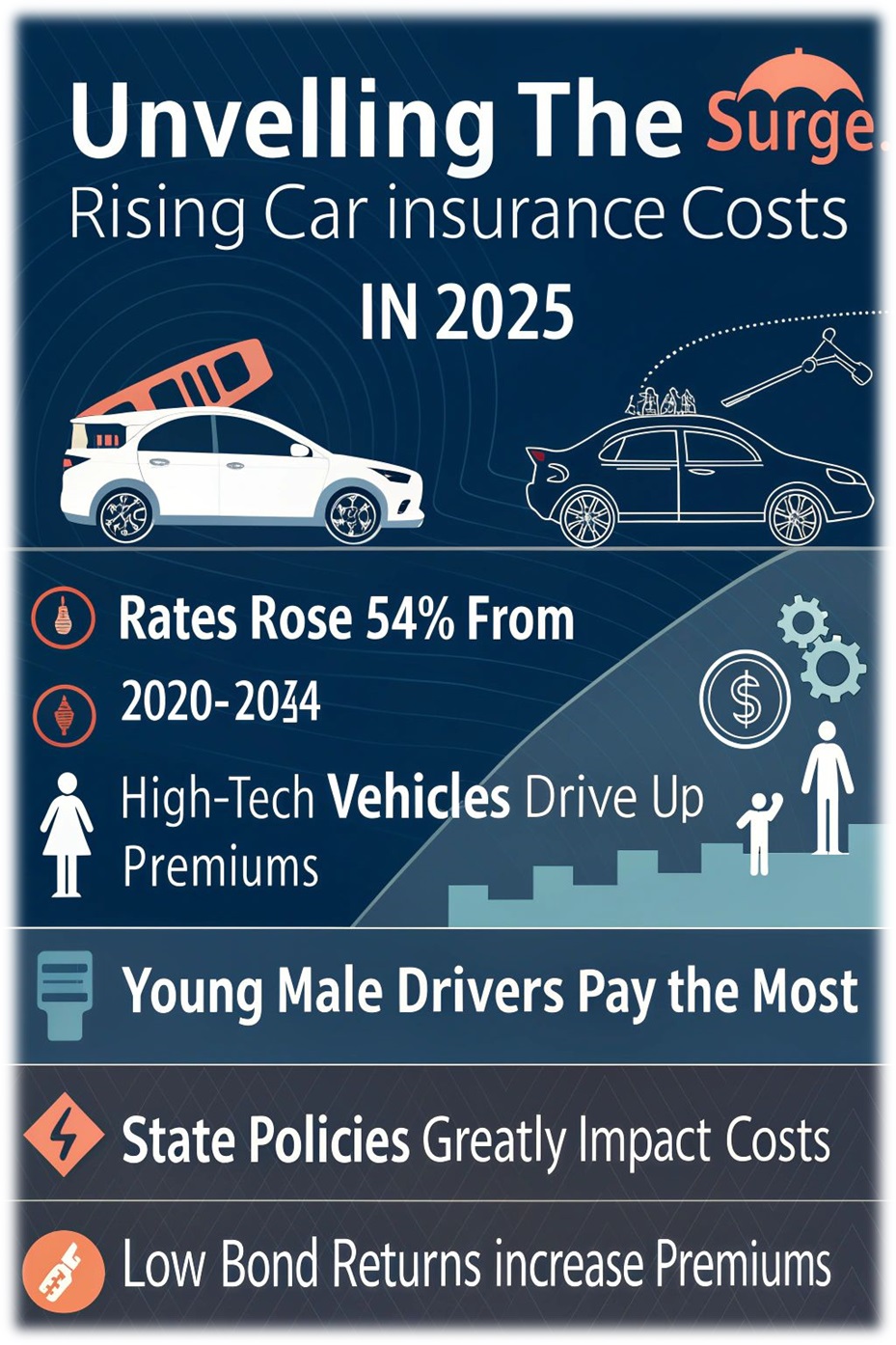
Do rising car insurance costs have your wallet feeling the pinch? Between 2020 and 2024, rates shot up by a staggering 54%, leaving many drivers struggling. This blog will break down why premiums keep climbing and what factors influence them.
Don’t miss out on tips to better understand these changes!
Factors Contributing to Rising Car Insurance Costs
Insurance prices are climbing, and drivers feel the pinch. Repair bills, investments, and market shifts are putting extra weight on auto insurers’ shoulders.
Inflation affecting repair and part costs
Rising inflation has pushed repair and part costs through the roof. In 2021, inflation hit 7%, followed by another spike of 6.5% in 2022. This made car parts like bumpers, mirrors, and sensors more expensive to replace.
Auto insurers now face higher claim payouts because repairs aren’t cheap anymore.
Labor costs have also climbed alongside part prices. A simple collision can result in steep bills for both insurers and drivers paying out of pocket. High-tech vehicles like Teslas are even costlier to fix due to advanced systems.
These price hikes directly impact your insurance premiums, making them harder on your wallet.
As cars get smarter, breakdowns get pricier.
Decreased returns from insurers' bond investments
Low returns from bond investments have hit insurance companies hard. The Federal Reserve's interest rate hike in 2022 caused bond values to fall. Insurers rely heavily on bonds for stable income, but now they earn less.
This affects their ability to cover claims without raising auto insurance rates.
Interest rate changes impact long-term planning for insurers. With smaller profits from bonds, they pass the burden onto car owners. Higher premiums for liability insurance or comprehensive coverage become unavoidable as insurers try to stay afloat financially.
Comparison of Motor Vehicle Insurance Rates and National Inflation Rate
Motor vehicle insurance costs are climbing at an alarming rate. The difference between their growth and the national inflation rate speaks volumes. Here's a snapshot of their trends:
|
Year |
Motor Vehicle Insurance Rate Increase (%) |
National Inflation Rate (%) |
Multiplier (Insurance vs. Inflation) |
|
1982 |
5.2 |
2.6 |
2x |
|
2000 |
6.8 |
3.4 |
2x |
|
2010 |
4.5 |
1.6 |
2.8x |
|
2024 |
13.7 |
5.1 |
2.7x |
Each entry uncovers how far apart these numbers have grown. In 2024, car insurance rates surged roughly 2.7 times faster than the average inflation rate. That gap's no small fry. It highlights the financial strain for the everyday driver. Rising repair costs, compounded by inflation, make matters worse. Each year tells a story, and most point to mounting costs.
Influencing Factors on Car Insurance Rates
Car insurance pricing depends on many personal details. These factors can boost or lower your monthly bill in surprising ways.
Age and Gender
Young drivers, especially males under 25, pay higher rates. They are seen as more likely to cause car accidents. Teen boys face the steepest premiums due to their risk on roads.
Insurance costs even out in middle age but rise again for seniors. Older adults may have slower reflexes or health issues that increase accident risks, raising insurance claims.
Marital Status
Married drivers often enjoy lower car insurance premiums. Insurance companies view them as less likely to cause accidents or file claims. Being married can show stability, which insurers reward with discounts.
Single drivers, meanwhile, may face higher rates. Some providers assume they are at greater risk on the road compared to their married peers. This difference affects both male and female policyholders across various states in the U.S., including large insurers like State Farm.
Vehicle Type
High-performance cars and luxury vehicles usually come with higher insurance premiums. Repairs for these cars are costly, and they face a higher risk of theft. For example, the cost to fix damaged parts on a leased or financed sports car can soar compared to repairs on a standard used car.
Trucks and SUVs might also see steep rates due to potential collision damage costs. Comprehensive insurance becomes important in such cases for protection against flooding or theft.
Vehicle type sharply impacts your auto accident coverage rate, leading directly into other contributing factors like location or driving history.
Location
Urban areas face steeper car insurance costs. Crowded streets, traffic jams, and higher crime boost risks for insurers. More accidents and thefts mean pricier premiums. For example, cities like Los Angeles and Chicago often have much higher rates than small towns.
Rural areas generally see lower premiums. With fewer cars on the road and less congestion, collisions are less likely. Lower crime in these regions also keeps costs down. Parking a car in a quiet rural town can save money compared to parking in a busy city center.
Driving Patterns
Longer commutes and more miles driven increased risk. This raises insurance premiums. For instance, a daily 40-mile commute doubles exposure to accidents compared to a 20-mile commute.
Traffic safety data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration shows higher crash rates in busy areas or during rush hours.
Aggressive driving like speeding or sudden stops also affects costs. A driver with multiple speeding tickets faces higher premiums than one without violations. Insurance companies factor these patterns into pricing, alongside location specifics covered next.
Driving Record
A poor driving record can make your car insurance skyrocket. Accidents, speeding tickets, and other violations stay on your record for years. Insurers see these as signs of risk, so they raise premiums.
If you’ve caused several car crashes or have DUIs, expect even higher rates.
Insurance companies use past behavior to predict the future. A clean history shows responsibility and lowers costs. Teens often face higher premiums because they lack experience and have more accidents statistically.
Keeping a spotless record helps save money in the long run––a single ticket could increase costs by hundreds each year!
Credit History
Credit history plays a big role in car insurance costs. Insurers check your credit report to judge risk. Low credit scores often mean higher rates, as companies see this as financial instability.
For example, someone with poor credit may pay hundreds more yearly than a person with excellent credit.
A strong credit score can lead to cheaper premiums. Many drivers bundle their home and auto policies to save even more money. Insurance agents also rely on data like the consumer price index or S&P 500 trends when assessing risks tied to finances.
Paying off debt and using a credit card wisely might improve your score—and lower your bill over time!
Economic and Regulatory Factors Affecting Auto Insurance Rates
Rising inflation shot up repair costs and part prices, leaving insurers to cover higher payouts. The Federal Reserve spiked interest rates in 2022, shaking the financial stability of many insurance companies.
Fluctuating returns from bond investments worsened this blow, making it harder for insurers to stay balanced.
State regulations also play a big role in setting rates. Some states cap how much premiums can rise while others allow more flexibility. For example, stricter rules may limit options like "get now pay later car insurance." These laws impact both what drivers pay and what companies can offer.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates on Insurance Premiums
Inflation pushes repair and part costs through the roof. Between 2020 and 2024, motor vehicle insurance rates jumped by 54%. Spikes in inflation during 2021 (7%) and 2022 (6.5%) worsened this trend.
As prices for labor and materials rose, insurers passed the burden to drivers with higher premiums.
Interest rates also play a part. Insurers earn from bond investments. Lower returns force them to adjust pricing strategies or increase premiums. This means families paying "get insurance now pay later" deals feel tighter budgets than ever before.
State-Specific Regulations and Insurance Rates
State laws greatly affect car insurance rates. Some states, with tight regulations, limit how quickly insurers can adjust prices. This keeps rate increases smaller but slows the process for market changes.
On the other hand, in more flexible states, companies can respond faster to risks like rising repair costs or higher claims.
Take California as an example—it often enforces strict rules to protect drivers from sudden hikes. Meanwhile, Florida allows insurers more freedom to set premiums based on higher risks like hurricanes or theft rates.
These differences mean buying car insurance isn’t just about your driving record; it’s also about where you live and local policies.
Age and gender also come into play—read on!
Conclusion
Car insurance costs are climbing fast, and drivers feel the pinch. Inflation, pricey repairs, and lower insurer profits share the blame. Your age, car type, and location all play a role in what you pay.
Staying safe on the road can help manage rising rates. It’s clear—2025 won’t make saving any easier!

