- January 2025 (2)
- December 2024 (3)
- November 2024 (4)
- October 2024 (5)
- September 2024 (4)
- August 2024 (6)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (6)
- May 2024 (5)
- April 2024 (6)
- March 2024 (5)
- February 2024 (3)
- January 2024 (7)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (4)
- October 2023 (7)
- September 2023 (4)
- August 2023 (5)
- July 2023 (4)
- June 2023 (4)
- May 2023 (6)
- April 2023 (4)
- February 2023 (7)
- January 2023 (6)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (6)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (6)
- July 2022 (3)
- June 2022 (3)
- May 2022 (4)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (3)
- February 2022 (4)
- January 2022 (4)
- December 2021 (4)
- November 2021 (6)
- October 2021 (6)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (6)
- July 2021 (8)
- June 2021 (5)
- May 2021 (5)
- April 2021 (3)
- March 2021 (2)
- February 2021 (4)
- January 2021 (1)
- March 2020 (1)
- July 2019 (1)
ThreatQuotient’s mission is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations with a platform that accelerates and simplifies investigations and collaboration within and across teams and tools.
To understand and stop threats more effectively and efficiently your existing security infrastructure and people need to work smarter, not harder. ThreatQ can serve as an open and extensible threat intelligence platform that accelerates security operations through streamlined threat operations and management. The integrated, self-tuning threat library, adaptive workbench and open exchange allow you to quickly understand threats, make better decisions and accelerate detection and response.
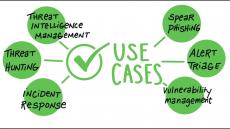
More than a Threat Intelligence Platform:
- Prioritize: Automatically score and prioritize internal and external threat intelligence based on your parameters.
- Integrate: Improve effectiveness of existing infrastructure by integrating your tools, teams and workflows.
- Automate: Automate aggregation, operationalization and use of threat intelligence across all systems and teams.
- Collaborate: Centralize threat intelligence sharing, analysis and investigation in a threat intelligence platform all teams can access.
Prioritize, automate & collaborate with a platform purpose-built for Threat-Centric Security Operations.